- to know the privileges and what it does - https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/security-access-control-privileges#all-privileges-alphabetical
- about table storage metric view - https://docs.snowflake.com/en/sql-reference/account-usage/table_storage_metrics
-
**[ ENCRYPTION = (TYPE = 'SNOWFLAKE_FULL' | TYPE = 'SNOWFLAKE_SSE') ]**Specifies the type of encryption supported for all files stored on the stage. You cannot change the encryption type after you create the stage.
**TYPE = ...**Specifies the encryption type used.Important
If you require Tri-Secret Secure for security compliance, use the
SNOWFLAKE_FULLencryption type for internal stages.SNOWFLAKE_SSEdoes not support Tri-Secret Secure.
Possible values are:
•
SNOWFLAKE_FULL: Client-side and server-side encryption. The files are encrypted by a client when it uploads them to the internal stage using PUT. Snowflake uses a 128-bit encryption key by default. You can configure a 256-bit key by setting the CLIENT_ENCRYPTION_KEY_SIZE parameter.
All files are also automatically encrypted using AES-256 strong encryption on the server side.
•
SNOWFLAKE_SSE: Server-side encryption only. The files are encrypted when they arrive on the stage by the cloud service where your Snowflake account is hosted.
Specify server-side encryption if you plan to query pre-signed URLs for your staged files. For more information, see
Types of URLs available to access files.
Default:
SNOWFLAKE_FULL -
The cloud platform you choose for each Snowflake account is completely independent from your other Snowflake accounts. In fact, you can choose to host each Snowflake account on a different platform, although this may have some impact on data transfer billing when loading data.
-
https://docs.snowflake.com/user-guide/data-sharing-multiple-db — data sharing form multiple dbs, this require the privilage REFERENCE_USAGE on DB.
-
By default, resource monitors can only be created by account administrators and, therefore, can only be viewed and maintained by them.
However, roles that have been granted the following privileges on specific resource monitors can view and modify the resource monitor as needed using SQL:
- MONITOR
- MODIFY
-
TYPE_OF — Returns the type of a value stored in a VARIANT column. The type is returned as a string.
-
Which privilege is required for a role to be able to resume a suspended warehouse if auto-resume is not enabled?
- OPERATE: Enables changing the state of a warehouse (stop, start, suspend, resume). In addition, enables viewing current and past queries executed on a warehouse and aborting any executing queries.
-
To specify the data retention period for Time Travel:
- The DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS object parameter can be used by users with the ACCOUNTADMIN role to set the default retention period for your account.
- The same parameter can be used to explicitly override the default when creating a database, schema, and individual table.
- The data retention period for a database, schema, or table can be changed at any time.
- The MIN_DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS account parameter can be set by users with the ACCOUNTADMIN role to set a minimum retention period for the account. This parameter does not alter or replace the DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS parameter value. However it may change the effective data retention time. When this parameter is set at the account level, the effective minimum data retention period for an object is determined by MAX(DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS, MIN_DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS).
-
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/intro-editions — sf editions and their features.
-
What effect does
WAIT_FOR_COMPLETION = TRUEhave when running an ALTER WAREHOUSE command and changing the warehouse size?WAIT_FOR_COMPLETION = FALSE | TRUE When resizing a warehouse, you can use this parameter to block the return of the ALTER WAREHOUSE command until the resize has finished provisioning all its compute resources. Blocking the return of the command when resizing to a larger warehouse serves to notify you that your compute resources have been fully provisioned and the warehouse is now ready to execute queries using all the new resources.
See this link.
-
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/sql-reference/constructs/sample#syntax — Sampling
-
While clustering a table, columns with which data types can be used as clustering keys?
- It can be any data type except GEOGRAPHY, VARIANT, OBJECT, or ARRAY
-
FLATTEN — https://docs.snowflake.com/en/sql-reference/functions/flatten#syntax
-
The unloading process automatically exports to multiple files so that it can take advantage of the parallelism offered by Snowflake. However, if needed, you can set the SINGLE parameter to true to ensure the export goes to a single file. The default size of each output file is 16 MB but can be changed using the MAX_FILE_SIZE parameter. The maximum allowed size per file is 5GB if you export data to cloud storage.
-
You can specify if a stored procedure runs under the caller’s or owner’s rights when creating the stored procedure. It defaults to the owner's right if nothing is specified. It is possible to change this configuration later by altering the stored procedure
-
Cloned objects are replicated physically rather than logically to secondary databases. That is, cloned tables in a standard database do not contribute to the overall data storage unless or until DML operations on the clone add to or modify existing data. However, when a cloned table is replicated to a secondary database, the physical data is also replicated, increasing the data storage usage for your account.
-
10% is discounted in cloud service layer in terms of costs(which is calculated daily)
-
Staged files cost based on size of the file(compressed or uncompressed)
-
A table with no micro-partitions (i.e. an unpopulated/empty table) has a clustering depth of ==
0== -
Columns are stored independently within micro-partitions, often referred to as columnar storage.
-
Columns are also compressed individually within micro-partitions.
-
Dropping a column does not immediately free up the column’s storage space.
- The space in each micro-partition is not reclaimed until that micro-partition is re-written. Write operations (insert, update, delete, etc.) on 1 or more rows in that micro-partition cause the micro-partition to be re-written. If you want to force space to be reclaimed, you can follow these steps: 1. CTAS 2. DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS 3. Drop the table
-
Time travel for MV is not supported, same goes to cloning but if schema/db is cloned/used for TT then MV will be there
-
Adding a column to the base table does not suspend a materialized view created on that base table.
-
Changing or dropping of columns will suspend MV, it can’t be resumed. it needs to be created again
-
renaming or swapping the base table will suspend the MV
-
dropping the base table will suspend MV but MV are not dropped immediately.
-
billing costs of MV can be viewed in MATERIALIZED_VIEW_REFRESH_HISTORY .
-
all warehouse and database object operations can be performed using the SYSADMIN role or lower roles in the hierarchy.
-
By default, not even the ACCOUNTADMIN role can modify or drop objects created by a custom role
-
The COPY_HISTORY view in the ACCOUNT_USAGE schema can be used to view history for data loaded through either the COPY command or continuous data loaded through Snowpipe.
-
Using the ACCESS_HISTORY view, you can identify what data was accessed, when, and who accessed it. Using this information, you can also identify what data is not being accessed at all.
-
To clone a table, you need SELECT privileges on the source table. For cloning Pipes, Streams & Tasks, you require OWNERSHIP privileges; for all other objects that can be cloned, you need the USAGE privileges.
-
LOGIN_HISTORY returns login events within a specified time range.
-
LOGIN_HISTORY_BY_USER returns login events of a specified user within a specified time range.
-
SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE shows from which IP address a user connected to Snowflake - LOGIN_HISTORY
-
The number of data files that can be processed in parallel is determined by the amount of compute resources in a warehouse.
-
ON_ERROR ; default values
- Bulk loading using COPY —
ABORT_STATEMENT - Snowpipe —
SKIP_FILE
- Bulk loading using COPY —
-
Snowflake appends what suffix that ensures each file name is unique while data unloading -(data_)
-
A User is running queries, A network policy is created and the user falls in the restricted list what will happen - Prevented from running further queries
-
How to monitor sensitive data for compliance, discovery, protection, and resource usage -
Tags -
What privilege can activate a network policy - Attach Policy privilege
-
Grants provided on a shared worksheet.
-
Who can grant privileges on managed access schema? -Only the schema owner (i.e. the role with the OWNERSHIP privilege on the schema) or a role with the MANAGE GRANTS privilege
-
unloading data copy into
VALIDATION_MODE = RETURN_ROWS (data that will be unloaded) -
Snowpark-optimized warehouses are recommended for workloads that have large memory requirements such as ML training use cases using a stored procedure on a single virtual warehouse node.
-
MAX_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL
- default - 8
-
STATEMENT_QUEUED_TIMEOUT_IN_SECONDS
- Amount of time, in seconds, a SQL statement (query, DDL, DML, etc.) remains queued for a warehouse before it is canceled by the system.
- default - 0
-
Query execution is maintained by which layer — processing layer
-
A materialized view cannot be created from a table if a row access policy is added to the underlying table.
-
A row access policy cannot be added to a table if a materialized view has been created from that underlying table.
-
Tasks - which privilege required to maintain and manage tasks - OPERATE
-
Where can you set min_data_retention_time_in_days - Account Level
-
Which Loop use break statement in scripting : Loop Scope
-
Future Grants are not supported - 1) sharing - these two will be answers.
-
All files are also automatically encrypted using AES-256 strong encryption on the server side.
-
Snowflake uses a 128-bit encryption key by default. You can configure a 256-bit key by setting the CLIENT_ENCRYPTION_KEY_SIZE parameter — this is for client side encryption
-
How to check failed user login attempts for the past 365 days ? Login_History in Account_Usage -
1-2 Q’s on Transfer role, creating default role and then deleting would result in which role similar tricky options [choose 2]
-
Snowflake allows a maximum number of 50 unique tags that can be set on a single object.
-
js procedure — $$ or ‘
-
parameter used to prevent stream from becoming stale - SYSTEM$STREAM_HAS_DATA
-
MAX_DATA_EXTENSION_TIME_IN_DAYS
- default - 14 days
- Maximum number of days for which Snowflake can extend the data retention period for tables to prevent streams on the tables from becoming stale. By default, if the DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS setting for a source table is less than 14 days, and a stream has not been consumed, Snowflake temporarily extends this period to the stream’s offset, up to a maximum of 14 days, regardless of the Snowflake Edition for your account. The MAX_DATA_EXTENSION_TIME_IN_DAYS parameter enables you to limit this automatic extension period to control storage costs for data retention or for compliance reasons.
-
Which among the following are Data Governing features available in all editions ? — OBJECT_DEPENDENCIES view
-
Privilege required for Search Optimization service - Ownership on table and Add Search optimization on schema
-
Session variables can only be used in a Javascript Stored Procedure when it’s created with Caller rights.
-
A single monitor can be set at the account level to control credit usage for all warehouses in your account.
-
In addition, a one or more warehouses can be assigned to a resource monitor, thereby controlling the credit usage for each assigned warehouse.
-
You can create multiple network policies, however only one network policy can be associated with an account at any one time.
-
auto suspend/resume warehouse which role is required - SYSADMIN - CREATE WAREHOUSE
-
Warehouse queuing can be identified using? WAREHOUSE_LOAD_METRCIS, WAREHOUSE_METERING_HISTORY
-
You must use the ACCOUNTADMIN role or another role with the CREATE DATABASE and IMPORT SHARE privileges to access a listing.
-
The table function REPLICATION_USAGE_HISTORY in Snowflake Information Schema can be used to query the replication history for a specified database within a specified date range. The information returned by the function includes the database name, credits consumed and bytes transferred for replication.
-
Snowflake doesn’t prunes micro-partitions based on a predicate with a subquery, even if the subquery result is constant.
-
==Temporary tables, stages, tasks, pipes, and external tables are not currently supported for replication.==
-
snowflake limits the size of query text (i.e. SQL statements) submitted through Snowflake clients — 1MB
-
The Snowflake web interface provides a convenient wizard for loading limited amounts of data into a table from a small set of flat files. the wizard is only intended for loading small numbers of files of limited size: 50 MB
-
Cloud providers apply data egress charges in which use cases:
- Data is transferred from one region to another within the same cloud platform
- Data is transferred out of the cloud platform
- Replicating data to a Snowflake account in a region or cloud platform different from where your primary (origin) Snowflake account is hosted.
- Using COPY INTO
to unload data to cloud storage in a region or cloud platform different from where your Snowflake account is hosted
-
AUTO_REFRESH_REGISTRATION_HISTORY table function can be used to query the history of data files registered in the metadata of specified objects and the credits billed for these operations. The table function returns the billing history within a specified date range for your entire Snowflake account. This function returns billing activity within the last 14 days.
-
Please note, STAGE_DIRECTORY_FILE_REGISTRATION_HISTORY table function can be used to query information about the metadata history for a directory table, including:
- Files added or removed automatically as part of a metadata refresh.
- Any errors found when refreshing the metadata.
-
Databases created from shares cannot be replicated.
-
Currently, when a database is dropped, the data retention period for child schemas or tables, if explicitly set to be different from the retention of the database, is not honored. The child schemas or tables are retained for the same period of time as the database. Similarly, when a schema is dropped, the data retention period for child tables, if explicitly set to be different from the retention of the schema, is not honored. The child tables are retained for the same period of time as the schema. To honor the data retention period for these child objects (schemas or tables), drop them explicitly before you drop the database or schema.
-
Object parameters are not replicated, except the parameter “DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS” for schemas & tables
-
The stream maintains only the delta of the changes; if multiple DML statements change a row, the stream records only the latest action taken on that row.
-
When a copy command cannot definitively determine whether a file has been loaded already, then what is the default behavior — file is skipped
-
Table stages don’t support transforming data while loading it (using a query as the source for the COPY command).
-
The Snowflake SQL API provides operations that we can use to:
- Submit SQL statements for execution.
- Check the status of the execution of a statement.
- Cancel the execution of a statement.
- Fetch query results concurrently.
Currently, Snowflake SQL API has limitations for the call command with stored procedures that return a table (stored procedures with the RETURNS TABLE clause).
-
An empty string is typically represented by a quoted empty string (e.g. ”) to indicate that the string contains zero characters. The preferred way is to enclose strings in quotes by setting the FIELD_OPTIONALLY_ENCLOSED_BY option, to distinguish empty strings from NULLs in output CSV files.
-
The warehouse performance can be evaluated by querying the Account Usage QUERY_HISTORY view.
-
What authentication methods does Snowflake support for REST API authentication? key pair and Oauth
-
SPLIT_TO_TABLE — This table function splits a string (based on a specified delimiter) and flattens the results into rows. SPLIT_TO_TABLE(
, ) -
SPLIT_PART — Splits a given string at a specified character and returns the requested part SPLIT_PART(
, , ) -
Snowflake stores metadata
- The range of values for each of the columns in the micro-partition.
- The number of distinct values.
- Additional properties used for both optimization and efficient query processing.
-
Snowsight supports the following types of charts:
- Bar charts
- Line charts
- Scatterplots
- Heat grids
- Scorecards
-
The connector creates the following objects for each topic:
- One internal stage to temporarily store data files for each topic.
- One pipe to ingest the data files for each topic partition.
- One table for each topic. If the table specified for each topic does not exist, the connector creates it; otherwise, the connector creates the RECORD_CONTENT and RECORD_METADATA columns in the existing table and verifies that the other columns are nullable (and produces an error if they are not).
-
Snowflake supports the following methods of authentication while using External API Authentication:
- Basic authentication.
- OAuth with code grant flow.
- OAuth with client credentials flow.
-
At what level can the ALLOW_CLIENT_MFA_CACHING parameter be set? Account
-
Which privileges are required for a user to restore an object? CREATE & OWNERSHIP
-
DOUBLE, DOUBLE PRECISION, REAL are synonymous with float
-
METADATAROW_NUMBER stage name columns
-
To determine the fully qualified URL and port for Snowsight, run the SYSTEM$ALLOWLIST function and review the
SNOWSIGHT_DEPLOYMENTentry in the return value. -
Streams can be created to query change data on the following objects:
- Standard tables, including shared tables.
- Views, including secure views.
- Directory tables.
- Event tables.
- External tables.
-
REST API which way of authentication is provided in general - Key pair authentication
-
Stages, Pipes,
-
If a role was specified as part of the connection and that role is a role that has already been granted to the connecting user, the specified role becomes the current role.
-
If no role was specified and a default role has been set for the connecting user, that role becomes the current role.
-
If no role was specified and a default role has not been set for the connecting user, the system role PUBLIC is used.
-
By default, the total number of reader accounts a provider can create is 20.
-
A network policy that is activated for a security integration does not restrict access to an internal stage.
-
Only security administrators (i.e. users with the SECURITYADMIN role) or higher or a role with the global ATTACH POLICY privilege can activate a network policy for an account.
-
ALLOW_CLIENT_MFA_CACHING - account level
-
Which privileges are required for a user to restore an object? — OWNERSHIP and CREATE
-
cloning
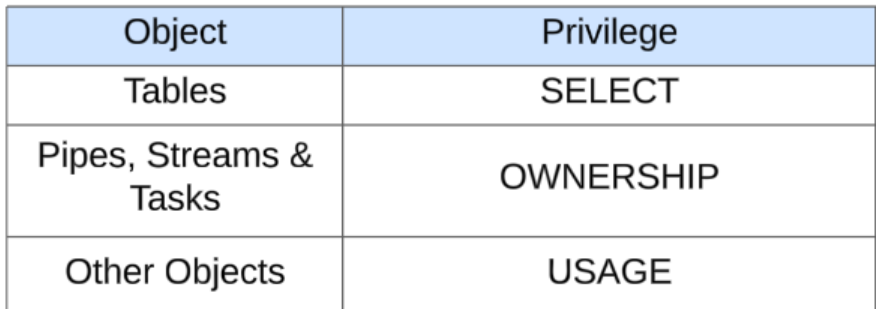
-
For better pruning and less storage consumption, we recommend flattening your OBJECT and key data into separate relational columns if your semi-structured data includes:
- Dates and timestamps, especially non-ISO 8601 dates and timestamps, as string values
- Numbers within strings
- Arrays
Non-native values (such as dates and timestamps in JSON) are stored as strings when loaded into a VARIANT column, so operations on these values could be slower and also consume more space than when stored in a relational column with the corresponding data type.
-
For text data types,
TYPEcan be used only to increase the length of the column. -
All unqualifed objects in a view or UDF definition will be resolved in the view’s or UDF’s schema only.
-
When calling the REST endpoints: Requires key pair authentication with JSON Web Token (JWT). JWTs are signed using a public/private key pair with RSA encryption.
-
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/data-load-snowpipe-intro#pipe-security
-
The smaller the average depth, the better clustered the table is with regards to the specified columns.
-
the role that executes the CREATE TASK command must have the global EXECUTE MANAGED TASK privilege
-
triggered task — Streams on Dynamic Tables, Iceberg Tables, Data Shares, Directory Tables, External Tables are not supported.
-
The Kafka connector relies on key pair authentication
-
Custom account roles can be created using the USERADMIN role (or a higher role) as well as by any role to which the CREATE ROLE privilege has been granted.
-
What are the primary authentication methods that Snowflake supports for securing REST API interactions? (Choose two.) - OAuth, basic